What is Cloud-Based ERP Software?
In today’s fast-paced digital landscape, businesses require agile, scalable, and cost-effective solutions to manage their operations efficiently. Cloud-based ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) software has emerged as a transformative solution, offering businesses a flexible and powerful way to integrate and streamline their processes. In this article, we explore what cloud ERP is, its benefits, security considerations, and future trends.
Understanding Cloud-Based ERP Software
Cloud ERP is a software solution that allows businesses to manage core business processes, such as finance, supply chain, manufacturing, HR, and customer relationship management (CRM), through a cloud-based platform. Unlike traditional on-premises ERP, which requires significant infrastructure investment and maintenance, cloud ERP is hosted on remote servers and accessed via the Internet.
Cloud ERP vs. On-Premises ERP
Understanding the differences between cloud ERP and on-premise ERP is crucial for businesses considering an ERP implementation.
| Feature | Cloud ERP | On-Premises ERP |
|---|---|---|
| Hosting | Hosted on vendor’s cloud servers | Installed on company-owned servers |
| Upfront Costs | Lower (subscription-based) | Higher (hardware & software licenses) |
| Maintenance | Managed by the vendor | Requires in-house IT management |
| Scalability | Easily scalable as business grows | Requires additional hardware for expansion |
| Security Updates | Automatic and vendor-managed | Requires manual updates and patching |
Cloud ERP provides greater flexibility and cost savings, making it the preferred choice for businesses aiming for growth and efficiency.
Why Businesses are Migrating to Cloud-Based ERP Systems?
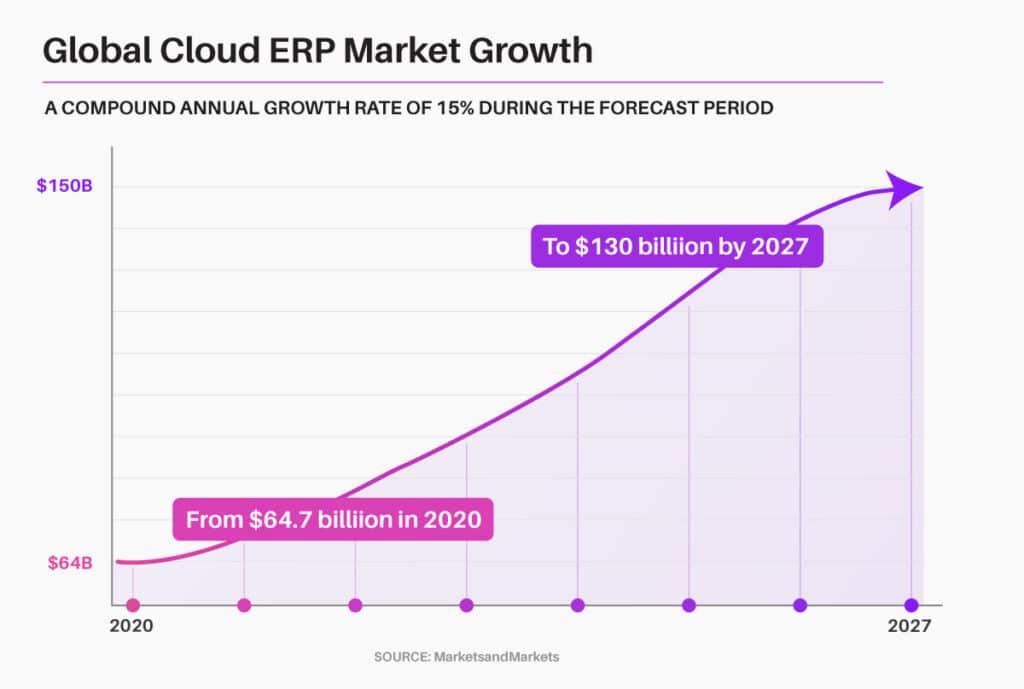
Businesses are rapidly shifting from traditional on-premises ERP solutions to cloud-based ERP systems due to the following key reasons:
Lower Total Cost of Ownership (TCO):
Cloud ERP eliminates the need for large upfront investments in IT infrastructure, reducing overall costs.
Faster Deployment & Implementation:
Businesses can deploy cloud-based ERP solutions quickly, allowing them to adapt to changing market conditions.
Remote Accessibility & Workforce Mobility:
Employees can access the ERP system from anywhere, promoting remote work and collaboration.
Scalability & Flexibility:
Cloud ERP grows with business needs, allowing seamless scalability without requiring additional IT resources.
Automatic Upgrades & Compliance:
The ERP provider ensures the system remains up-to-date with the latest security and compliance requirements.
Enhanced Security & Disaster Recovery:
Cloud ERP solutions offer built-in security features and backup options to protect business-critical data.
Types of Cloud ERP Solutions
Cloud ERP is not a one-size-fits-all solution. Different models cater to varying business needs:
Multi-Tenant SaaS –
A single software instance serves multiple customers, ensuring cost efficiency and easy upgrades.
Single-Tenant SaaS –
A dedicated software instance for each customer, offering enhanced control and customization.
Public Cloud ERP –
Hosted on shared cloud infrastructure, reducing costs.
Private Cloud ERP –
Dedicated infrastructure for a single organization, offering enhanced security and control.
Hybrid ERP –
A mix of on-premises and cloud solutions, allows businesses to transition gradually.
Key Benefits of Cloud-Based ERP
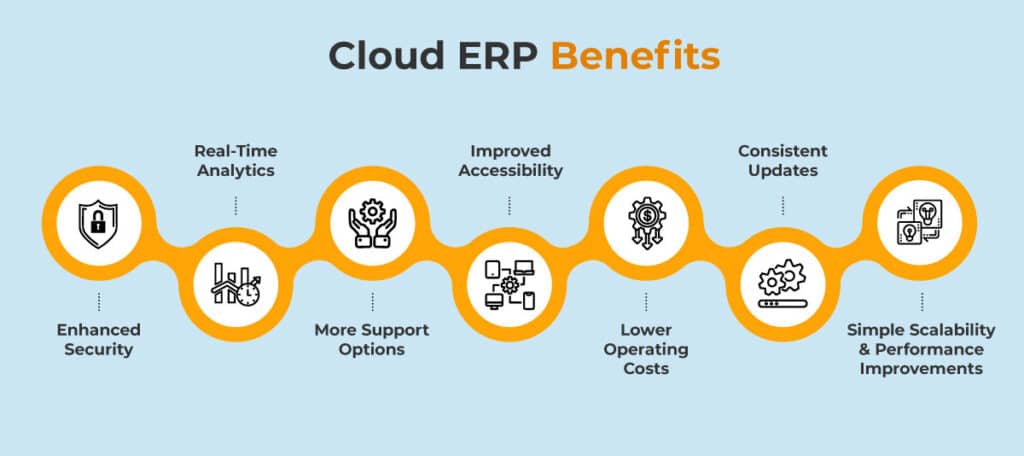
Cloud ERP offers several advantages over traditional ERP systems:
1. Cost-Effectiveness
- Eliminates upfront investments in IT infrastructure.
- Operates on a subscription-based pricing model.
2. Scalability & Flexibility
- Easily scales up or down to meet business demands.
- Supports multi-location and remote access.
3. Automatic Updates & Maintenance
- Software updates and security patches are handled by the vendor.
- Ensures compliance with evolving industry standards.
4. Enhanced Security & Compliance
- Data encryption and multi-factor authentication for secure access.
- Compliance with global data protection regulations such as GDPR.
5. Improved Business Continuity
- Cloud-based disaster recovery ensures minimal downtime.
- Data is backed up regularly for added security.
Security Considerations in Cloud ERP
Security is a critical concern for businesses migrating to the cloud. Leading cloud ERP providers implement advanced security measures, including:
End-to-End Data Encryption:
Ensuring data is protected during transmission and storage.
Regular Security Updates:
Vendors continuously update systems to address vulnerabilities.
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC):
Restricting access to authorized users only.
24/7 Monitoring & Threat Detection:
Real-time surveillance to prevent cyber threats.
Future Trends in Cloud ERP
As technology continues to evolve, cloud ERP systems are integrating cutting-edge advancements:
1. Artificial Intelligence (AI) & Machine Learning (ML)
- AI-powered analytics provide deeper business insights.
- Machine learning automates routine tasks and improves decision-making.
2. Internet of Things (IoT) Integration
- IoT-enabled ERP improves supply chain visibility.
- Real-time tracking of inventory and assets.
3. Blockchain for Enhanced Security
- Blockchain technology enhances data integrity and security in cloud ERP.
- Provides tamper-proof audit trails for financial transactions.
4. Enhanced User Experience (UX) with Automation
- Modern ERP solutions incorporate voice assistants and intuitive dashboards.
- AI-driven chatbots assist employees with real-time queries.

Conclusion
Cloud-based ERP software is revolutionizing the way businesses operate, offering enhanced flexibility, security, and scalability. By understanding the different deployment models, key benefits, and emerging trends, businesses can make informed decisions about their ERP strategy.
BatchMaster’s cloud ERP solution is designed to help businesses optimize their operations while leveraging the latest advancements in ERP technology. To learn more, visit our Cloud ERP solutions page.