Table Of Content
- Definition of Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)
- A Brief History of ERP Systems
- The Modern Face of ERP Systems:
- Why Businesses Need an ERP System?
- What to Look for in an ERP Software?
- What are the types of ERP Deployment?
- What are the Modules of an ERP System?
- Who Should Implement ERP System?
- Understanding ERP Software Integration
- Benefits of Enterprise Resource Planning System
- The Future of ERP Systems
Definition of Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)
Enterprise Resource Planning, also known as ERP software, is a business management software which helps businesses collect, store, manage and interpret data from different business activities in real-time.
The software comes with a set of integrated applications that helps with smooth functioning of entire business process.
This means, an ERP software has the capability to integrate different core processes of a business such as –
- Finance
- Supply chain
- Manufacturing
- Raw material procurement
- Marketing & sales
- Planning, etc. into a one single system
An ERP software facilitates the flow of real-time information across departments and empowers data-driven, proactive and accurate business decisions based on real facts.
ERP systems actually helps organizations get rid of multiple systems and processes, taking form of a unified IT package.
This way, it gives employees authorized access to the single-yet-shared database where data entered once can be used over and again.
It also eliminates data duplication, chances of errors, delays and manipulations and brings a degree of automation to the business.
It enables synchronized report generation based on key business metrics, so that businesses can achieve required information whenever they need and in the way they need.
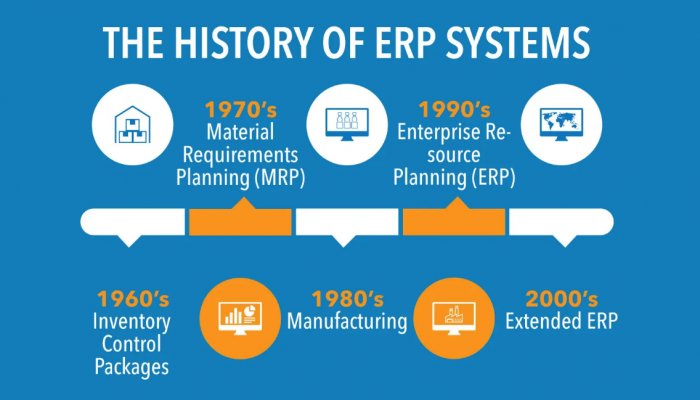
A Brief History of ERP Systems
Although paper-based systems resembling the basic functionalities of today’s ERP have existed since the 1910s, the first computer-based software close to ERP that we see today was developed by IBM in the 1960s with the help of Mr. J.I. Chase.
With the development of MRP II in the 1980s, ERP systems took a crucial step towards their current form. By 1990, research firm Gartner coined the term “Enterprise Resource Planning” and following this, ERP took its current form with a unified database.
Then, the introduction of cloud ERP in the early 2000s transformed the game with reduced upfront investment and predictable operating costs.
With companies not needing to install costly server’s on-premise or hire technical staff for operations, ERP system made its way into the factories of micro, small and mid-size manufacturers along with big corporations.
By increasing its scope with capabilities to integrate with other systems, ERP has now become essential for every manufacturing organization.
The Modern Face of ERP Systems:
Although it is still built with the basic purpose of shared information, the face of ERP software has completely changed.
Modern day ERP solutions have embraced technological advancements allowing businesses to control from anywhere and at any time via cloud, along with being available on-premise.
Not just industry-specific solutions, but availability of micro-vertical specific ones have drastically reduced the implementation time as well as the customization cost, while increasing the degree of fit in terms of processes and regulatory mandates.
Keeping pace with these improvements, an increasing number of vendors are coming up with ERP solutions that are fit for small businesses too, and are simple yet fast.
For ex., SAP Business One was designed for big enterprises, but now caters to smaller businesses too.
And with the advent of HANA, simplicity and speed of processing has gone up manifolds.
Moreover, the availability of online learning portals, e-courses, knowledge base and simplified workflows has substantially curbed the need for intensive training, which is one of the major concerns, fears and expenses for ERP adopters.
Why Businesses Need an ERP System?
Businesses need ERP system to achieve real-time visibility in their supply chain. The company can also zero-in on factors affecting their production output including material losses, process redundancies, workflow discrepancies and packaging errors.
A paper or spreadsheet-based system fails to track, raise alerts and perform corrective actions in case of any risk events.
The post-covid scenario also demands for the top quality products that are in-line with government and industry regulations. Regulations, that are changing day-in-day-out to ensure worker and consumer safety.
Staying at par with this dynamic environment through paper-based methods can be a road leading to recalls, customer dissatisfaction, brand defamation etc.
Industries can use an ERP solution to track the requisition and purchase of materials, ensure that the material is tracked at every step of the production process.
It can also record data related to enterprise workflows, business processes, reports and analytics in a unified database.
Thus, ERP systems should be implemented as a business solution to achieve maximum value from every organizational effort from each employee and every process.
The organization should eventually choose an ERP system which is:
Scalable
Capable of growing with the business
Flexible
Can adjust with changing business environment

Economic
Has an optimal ROI

Easy to Use
Convenient for the end-user

Mobile friendly
Able to run tablets, smartphones along with computers
Integration friendly
Can integrate with other systems
What to Look for in an ERP Software?
Every organization expects a newly implemented system to transform their business.
However, this doesn’t happen overnight. ERP system offers benefits, both tangible and intangible, which are experienced over a period of time, if and only if the choice of the ERP solution is right.
So, before choosing an ERP software, decision-makers should carefully evaluate their options, find the best fit for their organizational structure and consider the vendor’s experience & expertise. (Read blog to know more)
What are the types of ERP Deployment?
On-premise: : A traditional ERP software, or on-premises ERP, has a database that resides on an onsite server and hardware. It is managed by the IT staff of the company which has got it implemented.
Cloud: A Cloud ERP is provided as a service and hosted on vendor’s servers. In this case, the software and its data is managed centrally at a remote datacenter (internet “cloud”) by the ERP vendor and accessed by customers through a Web browser.
Hybrid: A hybrid ERP solution is the combination of the two ERP – on-premise & cloud. By opting for a hybrid ERP, a company can adopt cloud applications while also retaining its on-site ERP resources. Greater mobility, ease of installation and outside support are some of the benefits that make businesses choose hybrid ERP software.
What are the Modules of an ERP System?
The key components of an ERP software are the multiple modules, with each of them focusing on one specific area of the business.
These modules are individually purchased, based on the specific needs and technical capabilities of the organization.
Some of the most common ERP modules include those for:
 Sales
Sales Production
Production Marketing
Marketing Quality Control/Assurance
Quality Control/Assurance Inventory Management
Inventory Management Accounting
Accounting Planning
Planning CRM
CRM Material Procurement
Material Procurement Formulation, BOM, R&D
Formulation, BOM, R&D Finance
Finance Business Intelligence
Business IntelligenceWho Should Implement ERP System?
Earlier, ERP systems were developed to manage discrete manufacturing processes which involved production of goods that are easily distinguishable and can be physically counted like nuts, bolts, wires, etc.
They were ideal for industries manufacturing automobiles, mobile phones, furniture, toys, etc. But with time, the need for software grew for process manufacturing too. As this industry is based on formulas/recipes and involves blending, mixing, heating, etc. it requires a software that follows production on assembly lines.
A dedicated ERP software for process manufacturing came into existence with key important features like –
- Physical property analysis
- Formulation
- Unit of measure conversion
- Density calculations
- Batch processing, etc. Among many.
So, be it any businesses, large-scale, small-scale or medium-sized, ranging from manufacturing to catering, using discrete or process manufacturing, needs an ERP solution.
It is because the challenges of small/medium businesses are no different from large industries.
They need to follow the same guidelines, stick to the same regulations, maintain reports & documents, meet quality parameters, manage resources, cut costs, thrive on thin profit margins et al, just like the big daddies of business.
Understanding ERP Software Integration
A manufacturing organization may feel the need to install multiple software to manage various business functions, and an ERP can be integrated with such software to extend its capabilities to these independent systems.
The user won’t have to deal with disconnected systems and fragmented data after ERP implementations.
It also integrates other systems like QMS, PLM, MES, CRM, HCM, eCommerce platforms, industry specific solutions and even other ERPs.
Customized adapters such as EDIs and APIs can be used to integrate ERP with other systems.
An ESB (Enterprise Service Bus) and iPaas (Integration Platform as a service) can come in handy for ERP integration to eCommerce, IoT (Internet of Things) and machine learning platforms.
iPaaS can also help with custom API generation, machine learning data integration, prebuilt content and a lot more.
ERP software integration helps in reducing the potential for inefficient workflows through its centralization of information.
Benefits of Enterprise Resource Planning System
An ERP software helps your business with numerous benefits, automation being the first. Check out the other:
Streamlined processes:
An ERP system integrates all the processes across departments from beginning to end and meets the specific needs of each individual business.
Improved productivity & efficiency:
An ERP system automates manual business tasks and processes to promote productivity and improve efficiency which in return saves time and money.
82 percent* companies that implemented an ERP solution improved either key or all business processes post implementation.
Enhanced business visibility:
ERP provides comprehensive and real-time visibility into performance of each department and access to key business data by integrating all business processes.
Quality analysis & reporting:
An ERP software allows business managers to use dashboards to analyze & report, for making quick, informed and accurate decisions.
Reduced costs & risks:
ERP systems reduce the operational and management costs by streamlining business processes whereas improves data integrity and financial by reducing risks.
Industry & regulatory compliance:
An ERP solution facilitates control over reporting processes, ensures compliance with regulatory requirements, meets data integrity and enables complete traceability.
This way, it keeps hefty fines and image damage. Studies reveal that,
54 percent* of the organizations that got the ERP implementation done were very satisfied with the overall ERP vendor experience.
Further,
57 percent* of the companies who got the ERP implementation done viewed it as a success
This should give you a clear picture as to how beneficial ERP is to the success of businesses.
The Future of ERP Systems
In the last century, ERP has evolved a lot and is adopting latest technological trends as well as advanced tools to resolve complex business problems.
However, ERP vendors continue to evolve by offering more powerful, flexible and affordable, all the time.
Some of the future trends that will define the future of ERP are:
- Cloud Technology
- Big data analytics
- IoT (Internet of Things)
- Artificial Intelligence
- Mobility,
- Integration with e-Commerce and,
- Move towards public cloud.
These trends will continue to make the businesses simpler.
And in all these years, the unprecedented response it has received and the faith which manufacturers across the globe have demonstrated in ERP, tells that ERP is here to stay for many more years to come.